Run a Coding query
Coding queries can help you to test ideas, explore patterns and see the connections between the themes, topics, people and places in your project. This topic explains how you can create Coding queries and what you can do with the results of the query.
What do you want to do?
- Understand Coding queries
- Create a simple Coding query using the Wizard
- Create a simple Coding query outside the Wizard
- Create an advanced Coding query
- Examples of Coding query criteria
- Understand the results
- Save the preview results as a node
- Use a Compound query to refine your Coding query
Understand Coding queries
To see what has been coded at a node, you can simply open the node (double-click in List View). You can use Coding queries to find content coded at selected nodes, a combination of nodes, or cases with particular attribute values.
You could use a Coding query to:
-
Gather material coded at combinations of nodes—for example, gather content coded at green policy and conservative government and explore the associations.
-
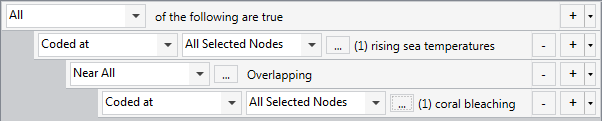
Gather material from cases with specific attribute values—for example, gather content coded at coral bleaching where it overlaps with content coded at rising sea temperatures.
If you are using NVivo Pro or NVivo Plus, you can also use a Coding query to:
-
Search for content coded at multiple nodes and use operators to further refine the query—for example, what do young farmers say about alternative energy?
-
Search for content that is not coded at a specific node—find content coded at solar power but not coded at alternative energy.
If you run a Coding query created in a different edition of NVivo, it may search sources that aren't supported in your edition. You will see accurate results but you won't be able to open or view some references. Refer to About queries (Working with queries across editions) for more information.
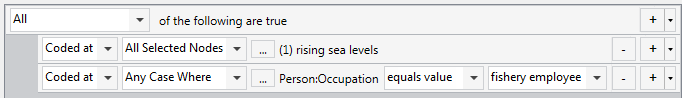
NOTE A coding query will only find content that has been coded. For example, if you ask the question what do fishery employees say about rising sea levels?—make sure you have coded source content at the node rising sea levels and at nodes with the attribute fishery employee.
Create a simple Coding query using the Wizard
This video describes how to create and run a Coding Query within the Wizard.
-
On the Query tab, in the Create group, click Query Wizard.
The Query Wizard opens. Follow the steps on the Wizard.
| Wizard step | Description |
|
Choose the query you want to run. |
Click Search for content based on how it is coded. |
|
Specify the content you want to search for. |
Find content that
is coded at:
|
|
Choose where you want to search. |
Choose whether you want to look for coded content in all your sources, or restrict the search to selected items or folders. |
|
Choose whether to add the query to your project. |
You can run the query once or choose to add it to your project (and run it). If you choose to add it to your project, you must enter a name. You can optionally enter a description. |
-
Click Run.
The query is executed and the results are displayed in Detail View.
Create a simple Coding query outside the Wizard
-
On the Query tab, in the Create group, click Coding.

A new blank query opens in Detail View.
-
Choose where you want to search for coding:
- All sources—search for content in all the sources in your project, including externals and memos
- Selected Items—restrict your search to selected items (for example, a set containing interview transcripts)
- Selected Folders—restrict your search to content in selected folders (for example, a folder of interview transcripts)
-
By default, the query will look for content where All of the rows of criteria are met. Select Any if you want content that meets only some of your criteria.
-
Define your criteria. You can find content that is coded at (or not coded at):
-
All Selected Nodes—find content that is coded at one or more nodes you specify. For example, find content coded at the node economy, or you might choose to find content that has been coded at the nodes negative and natural environment—this option uses the AND operator. Click the
 button to select the node.
button to select the node. -
Any Selected Node—find content coded at any of the nodes you specify. For example, find content that has been coded to any of the nodes habitat, forest or landscape—this option uses the OR operator. Click the
 button to select the nodes.
button to select the nodes. -
Any Case Where—find content coded at cases with specific attribute values. For example, you could search for content coded at males aged 25-35. Click the
 button to select the attribute values.
button to select the attribute values.
-
(Optional) In the Spread to list, define the spread coding options (amount of coding spread around the search word). Refer to Spread coding for more information.
-
Click the Run Query button.
NOTE
-
To save the Coding query, select the Add to Project check box.
-
Use the Save Results button to store the query results—for example, you might want to store the results as a node when you run the query. Refer to Query options for detailed information.
Create an advanced Coding query
This feature is available in NVivo Pro and NVivo Plus.
You can create more advanced coding queries to search for source content that has been coded at multiple nodes—and use operators to further refine the search.
-
On the Query tab, in the Create group, click Coding.

A new blank query opens in Detail View.
-
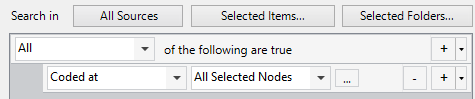
In the query panel, follow the steps to build the query criteria:
-
Choose where you want to search for coding:
- All sources—search for content in all the sources in your project, including externals and memos
- Selected Items—restrict your search to selected items (for example, a set containing interview transcripts)
- Selected Folders—restrict your search to content in selected folders (for example, a folder of interview transcripts)
- By default, the query will look for content where All of the rows of criteria are met. Select Any if you want content that meets only some of your criteria.
- Define your criteria. You can find content that is coded at (or not coded at):
-
All Selected Nodes—find content that is coded at one or more nodes you specify. For example, find content coded at the node economy, or you might choose to find content that has been coded at the nodes negative and natural environment—this option uses the AND operator. Click the
 button to select the node.
button to select the node. -
Any Selected Node—find content coded at any of the nodes you specify. For example, find content that has been coded to any of the nodes habitat, forest or landscape—this option uses the OR operator. Click the
 button to select the nodes.
button to select the nodes. -
Any Case Where—find content coded at cases with specific attribute values. For example, you could search for content coded at males aged 25-35. Click the
 button to select the attribute values.
button to select the attribute values.
- Click the down arrow on the
 button to build or manage
your search criteria:
button to build or manage
your search criteria:
-
Add group—add a new group of criteria rows beneath the current row.
-
Add row—add a new criteria row beneath the current row.
-
Coded by any—select coding done by any user or choose only the coding done by specific users. Click the
 button to select
the users.
button to select
the users. -
Near—gather coded content that is near other coded content. Click the
 button to specify proximity.
button to specify proximity. -
Move up and Move down—change the order of processing. Criteria at the top of the list are processed first.
-
(Optional) In the Spread to list, define the spread coding options (amount of coding spread around the search word). Refer to Spread coding for more information.
-
Click the Run Query button.
NOTE
-
To save the Coding query, click the Add to Project button.
-
Use the Save Results button to store the results—for example, you might want to store the results as a node when you run the query. Refer to Query options for detailed information.
-
Click the
 button to remove a criteria
row from your query.
button to remove a criteria
row from your query.
Examples of Coding query criteria
This feature is available in NVivo Pro and NVivo Plus.
The following examples show how you can build advanced query criteria to answer specific questions:
| To answer the question | Do this |
| What do fishery employees say about rising sea levels? |
Build a query where all of the following are true:
|
| Is there a connection between rising sea temperatures and coral bleaching? |
Build a query where all of the following are true:
|
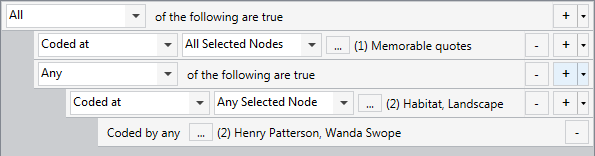
| What memorable quotes have Henry or Wanda found about habitat or landscape ? |
Build a query where all of the following are true:
|
Understand the results
By default, the results of a Coding query are displayed as a node in Detail View—the Reference tab is in focus:
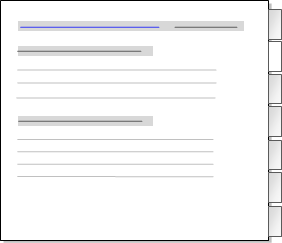
Click the tabs on the right to see the content that has been coded in text (documents, memos and externals), PDF, audio, video, picture or dataset sources.
By default the results are displayed in a preview node—you can choose to save this node in the Results folder or in another node folder, refer to Save the preview results as a node for more information.
NOTE
-
If you prefer nodes to open with the Summary tab in focus, you can change the setting in Application Options.
-
If you include an 'aggregate' node in the scope of a query, content coded at the node and all its direct children will be included in the query results—refer to Aggregate nodes for more information.
Save the preview results as a node
If your query has returned interesting content, you may want to save it as a node, so that you can explore it further. For example, you might find all the content coded at both the nodes water quality and the node development. You can save the results to a new node that holds your evidence that Development negatively impacts water quality.
The node will contain the content displayed on the Reference tab in the query results in Detail View. If you repeatedly run the same query, you may want to merge the references into an existing node, rather than create them as a new node.
To save the references as a node:
-
Click on the query results in Detail View.
-
On the Query tab, in the Actions group, click Store Query Results.
The Store Query Results dialog box opens.
-
From the Option list, choose what you want to do with the results. You can:
-
Create the results as a new node
-
Merge the results into an existing node (you must select the node to merge into)
-
If you are creating a new node, enter a name and description.
-
Click OK.
NOTE
-
By default new nodes are created in the Results folder, unless you choose another location. Refer to Manage query results (Understand the Results Folder), for more information.
-
If you save the results as a node hierarchy, relevant content from each source is coded to a separate node, under a parent node.
-
You can choose how you want to store the results before you run the query—by setting your preferences on the Query Options tab in the query properties.
Use a Compound query to refine your Coding query
This feature is available in NVivo Pro and NVivo Plus.
You can use a Compound Query to further refine a Coding query, for example you could:
- Combine two Coding queries to find content coded at Node A when it precedes content coded at Node B
- Combine a Coding query with a Text Search query to find text in relation to coding—where young women talk about climate change, do they use the word pessimistic?